Contact
Katie Teague (kteague@uada.edu)
Jane Maginot (jmaginot@uada.edu)
Kristen Crawley (kcrawley@uada.edu)
Construction Best Management Practices (BMPs)
Improperly managed construction sites can cause erosion and lead to water pollution from stormwater runoff.
Use these best management practices, or BMPs, to protect local streams and rivers:
- Stabilized Construction Exit
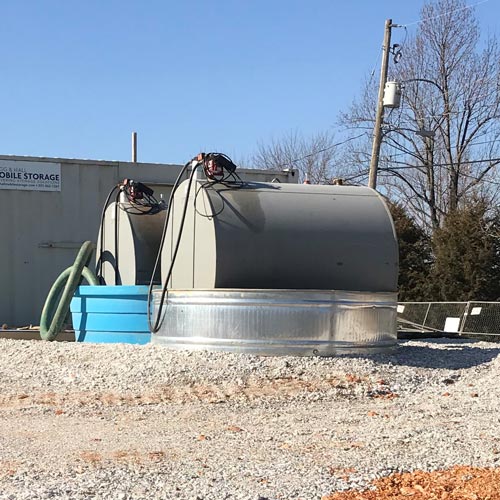
- Secondary Containment
- Silt Fence
- Concrete Washout
- Check Dam
- Straw Wattle
- Site Stabilization
- Inlet Protection
- Street Sweeping
- Trash Management
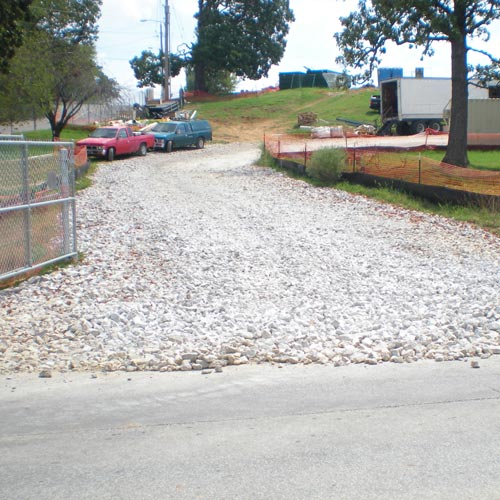
Stabilized Construction Exit
A Stabilized construction exit is also known as a track pad or vehicle tracking pad.
These are temporary structures located at the entrance/exit of a construction site
that remove and capture sediment/dirt from truck tires as they pass. Stabilized construction
exits keep public streets clean and sediment out of storm drains.
Learn more about stabilizing the exit
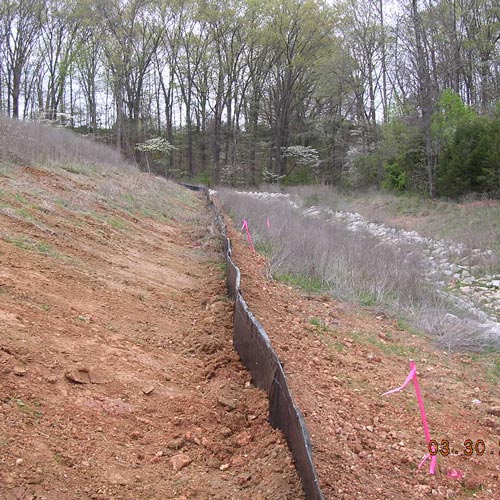
Silt Fence
Silt fences are made of filter fabric that has been entrenched, attached to supporting poles, and sometimes backed by a plastic or wire mesh for support. The silt fence slows and ponds stormwater which allows sediment to settle out before the stormwater leaves the site. Silt fencing works only if it is installed and maintained properly. Maintenance includes checking the fence after each rainfall, looking for gaps and tares (replace if needed), and removing accumulated sediment once the sediment level reaches 1/4 to 1/3 the height of the fence.
Concrete Washout
Concrete washouts are leakproof containers that collect and retain both water and solids during the washout process. Trucks must rinse their equipment and hand tools before the leftover concrete hardens. Wash water is caustic (high pH) and full of fine particles which can contain metals. This best management practice (BMP) is intended to eliminate concrete process water and slurry from leaving the construction site and polluting local waterbodies. Wash water and leftover product shall be contained in a lined container. The container can be single-use or re-usable if the concrete is completely contained. Contained concrete shall be disposed of in a manner that does not violate groundwater or surface water quality standards.
Check Dam
Check dams are temporary structures constructed within concentrated-flow areas such as ditches or channels. Check dams create ponding and disperse the energy of the runoff. This has two benefits: 1. sediment carried by flowing water will settle out behind dam structure and 2. reduced energy reduces erosion potential.
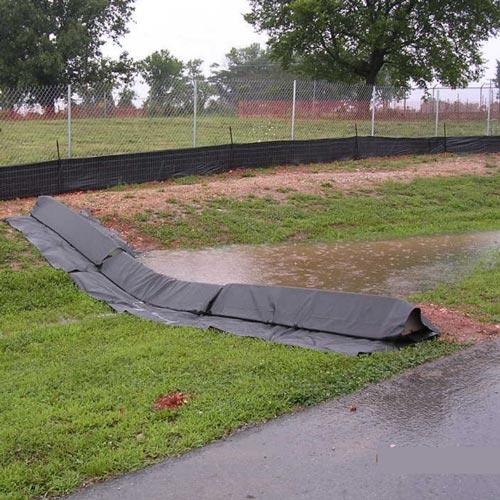
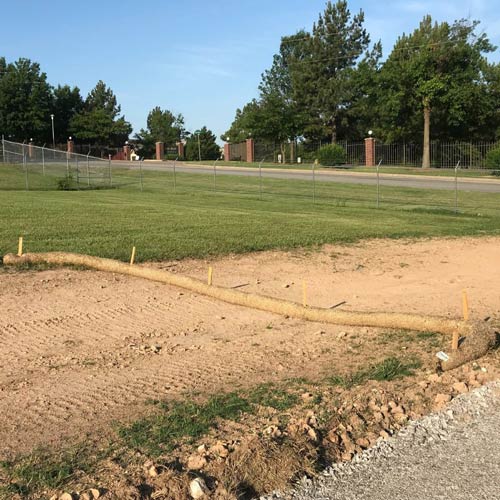
Straw Wattle
Straw wattles are intended for low surface flow areas such as hillsides or streambanks. They are not intended for high surface flow areas such as ditches or channels. When installed and spaced properly, straw wattles slow stormwater and spread it out. Straw wattles will capture some sediment behind the wattle where ponding water allows sediment to settle out. Wattles should be trenched in and overlapped at connections. Spacing between wattles is based on slope.
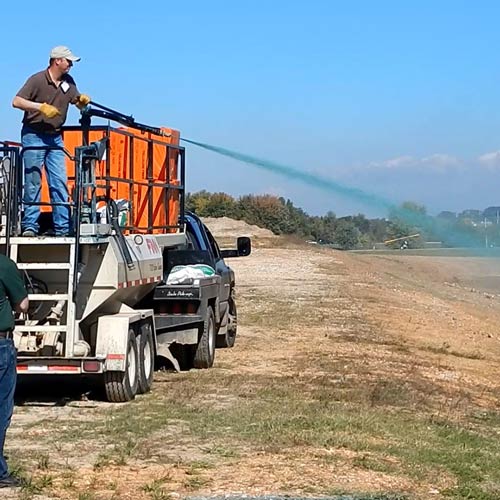
Site Stabilization
Hydroseeding is used to quickly establish permanent vegetative cover which controls erosion in a construction zone. Hydroseeding uses cellulose fibers or mulch, seeds of desired vegetation species, green dye, and fertilizers. These items are mixed into a slurry and sprayed onto disturbed soil using a hydroseeder. Hydroseeding is cheaper than laying sod and more effective and successful than seed and straw. Hydroseeding contains polymers that help hold moisture where it is needed thus reducing the amount of watering.
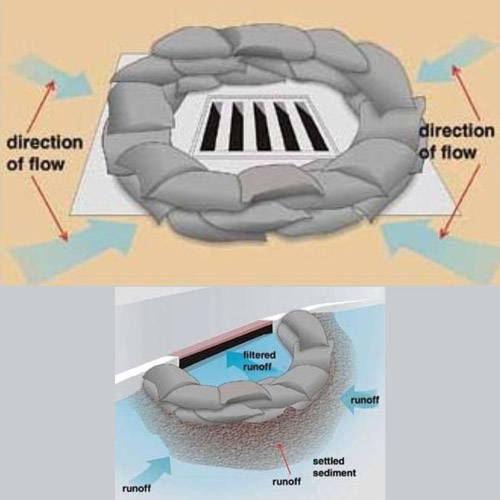
Inlet Protection
Inlet protection is typically the last line of defense for keeping sediment and debris from leaving the construction site and entering a stream, river, or lake. Inlet protection are temporary structures that allow storm drain inlets on a construction site to remain operational prior to permanent site stabilization. External inlet protection (as pictured) creates ponding. Ponding allows sediment to settle out. Water slowly filters through the inlet protection structure which can be made of gravel, stone, or fabric. Inlet protection is always a secondary control device meaning it should always be used in conjunction with other sediment and erosion control practices.
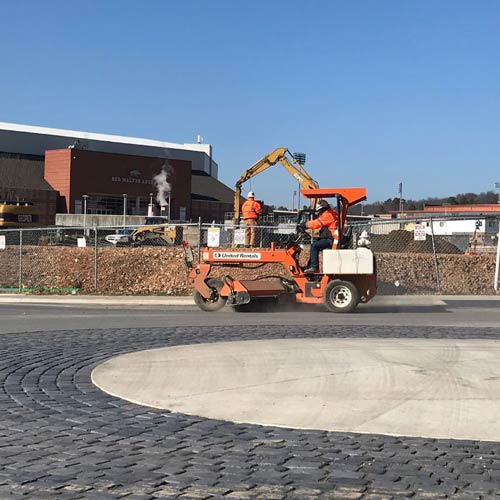

Street Sweeping
Even after trucks and equipment drive over the stabilized construction exit, some dirt and dust are carried to the street. Street sweeping the paved area adjacent to the stabilized construction exit will be required periodically. Wet weather will likely lead to increased sweeping and maintenance.
Want to stay updated on construction best management practices?