Plant Board expands Emerald Ash Borer quarantine to include 33 counties in state
By Ryan McGeeney
U of A System Division of Agriculture
Oct. 3, 2016
Fast Facts:
- Emerald Ash Borer first confirmed in Arkansas in 2012
- Now confirmed in eight counties throughout Arkansas, most recently in Randolph County
- Quarantine zone intended to create buffer and protect other counties in state
(563 words)
(Newsrooms with art: Downloadable ASPB quarantine map available at https://flic.kr/p/MELVrq)
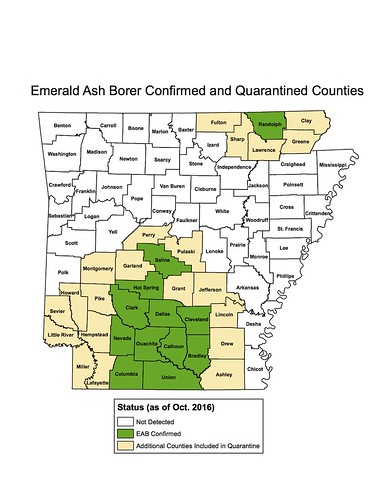
LITTLE ROCK — The Arkansas State Plant Board moved last week to expand the emerald ash borer quarantine to include 33 counties throughout the state. The expansion adds eight new counties to the quarantine list, including Randolph County, where the presence of the invasive pest was recently confirmed, as well as the five counties that border it within the state: Fulton, Sharp, Lawrence, Greene and Clay counties.
Pulaski and Perry counties have also been added to the 2014 list of quarantined counties designed to isolate the 11 counties in south central Arkansas where the invasive beetle has previously been confirmed, including Saline, Hot Spring, Clark, Dallas, Cleveland, Nevada, Ouachita, Calhoun, Bradley, Columbia and Union counties.
Randolph County is the 12th county in which the emerald ash borer has been confirmed.
The expanded quarantine zone effectively creates a county-wide buffer between the two areas in which the beetle has been confirmed — the block of 11 counties in south central Arkansas, as well as Randolph County in the northeast — and the state’s remaining 48 counties in which the beetle has not been detected.
It is illegal to transport certain items from within the quarantine zones to areas outside the zones. According to the Arkansas Department of Agriculture, quarantined items include firewood of any hardwood species, as well as ash tree products including:
- Nursery stock
- Green lumber with bark attached
- Living, dead, cut or fallen logs
- Pulpwood, stumps, roots, branches
- Mulch and composted or uncomposted chips greater than 1 inch in diameter
Randolph County Cooperative Extension Service office chair Mike Andrews said the State Plant Board informed him of the beetle’s confirmed presence in his county in early August, but that he hadn’t heard from any residents who were concerned they might be seeing an infestation.
“I’ve put out information with the local media — newspaper and radio,” Andrews said. “If they think they might have a problem, we’re ready to get them all the information they need.”
Signs of infestation include:
- Multiple jagged holes excavated by woodpeckers feeding on ash borer larvae
- Distinctive D-shaped exit holes left by emerging adult beetles
- Canopy dieback from top of tree
- Sprouts arising from the base of the tree
- Larval tunnels or galleries immediately under the bark of dying ash trees
Chandler Barton, a forest health specialist with the Arkansas Forestry Commission, said the AFC and the State Plant Board are currently developing control measures for the beetle by establishing parasitoid wasp populations at three sites in Arkansas, including Logoly State Park, White Oak State Park and on a private property near Arkadelphia.
“It typically takes about three years to establish the wasp population,” Barton said. “On the third year following the first introduction, we sample for the wasp to determine establishment and monitor its effect on the emerald ash borer.”
Barton said the wasps were imported from Asia to a facility operated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service in Brighton, Michigan. This facility raises the wasps for biocontrol purposes and shares them with partners across the United States, he said.
For more information about the emerald ash borer, visit www.emeraldashborer.info or www.arinvasives.org. A fact sheet about the borer may be found at: “Emerald Ash Borer: A potential pest of ash trees in Arkansas”, downloadable at www.uaex.uada.edu/publications/pdf/FSA-7066.pdf. To learn more about treatment options for homeowners who suspect they may have an emerald ash borer infestation, contact your local county extension agent, or visit http://www.uaex.uada.edu/.
Pursuant to 7 CFR § 15.3, the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture offers all its Extension and Research programs and services (including employment) without regard to race, color, sex, national origin, religion, age, disability, marital or veteran status, genetic information, sexual preference, pregnancy or any other legally protected status, and is an equal opportunity institution.
# # #
Media Contact: Mary Hightower
Dir. of Communication Services
U of A Division of Agriculture
Cooperative Extension Service
(501) 671-2126
mhightower@uada.edu
Related Links